WebRTCブログ第一回

はじめまして!OISの自社製品『ReDois』開発担当です。
『ReDois』は、WebRTCと呼ばれる技術を利用し、リアルタイム配信を実現しています。

私からは、このWebRTCに関する情報について発信していこうと思います。
今回は、WebRTCの基本として、P2Pでの接続について解説します。
WebRTC公式より公開されているサンプルページを使い、ソースコードの解説も交えながら見ていこうと思います。
ソースコードはこちらになります。
このサンプルページでは、左上から順にボタンを押していけば自分同士でWebRTC接続ができるようになっています。
それぞれのボタンを押したとき、具体的にどのような動作をしているのか掘り下げていきましょう。
①[Get media]ボタン
最初に、マイクやカメラからストリームを取得し、それを画面に表示します
async function getMedia() {
(中略)
try {
const userMedia = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia(constraints);
gotStream(userMedia);
} catch (e) {
console.log('navigator.getUserMedia error: ', e);
}
}
function gotStream(stream) {
console.log('Received local stream');
localVideo.srcObject = stream;
localStream = stream;
}
具体的には、
navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia()メソッドでMediaStreamオブジェクトを取得し、これを画面上のvideo要素にセットすることによってマイクやカメラの音声・映像をブラウザ上で再生することができます。
(サンプルページでは、localVideoが示すvideo要素はmuted属性を持っているので音声は再生されません)
②[Create peer connection]ボタン
WebRTC接続の要となるオブジェクトである、RTCPeerConnectionオブジェクトを作成します。
function createPeerConnection() {
(中略)
const servers = null;
window.localPeerConnection = localPeerConnection = new RTCPeerConnection(servers);
console.log('Created local peer connection object localPeerConnection');
localPeerConnection.onicecandidate = e => onIceCandidate(localPeerConnection, e);
sendChannel = localPeerConnection.createDataChannel('sendDataChannel', dataChannelOptions);
sendChannel.onopen = onSendChannelStateChange;
sendChannel.onclose = onSendChannelStateChange;
sendChannel.onerror = onSendChannelStateChange;
window.remotePeerConnection = remotePeerConnection = new RTCPeerConnection(servers);
console.log('Created remote peer connection object remotePeerConnection');
remotePeerConnection.onicecandidate = e => onIceCandidate(remotePeerConnection, e);
remotePeerConnection.ontrack = gotRemoteStream;
remotePeerConnection.ondatachannel = receiveChannelCallback;
localStream.getTracks()
.forEach(track => localPeerConnection.addTrack(track, localStream));
console.log('Adding Local Stream to peer connection');
}
今回は自分同士での接続なので、ローカル・リモート共にこの場でRTCPeerConnectionオブジェクトを作成しています。
RTCPeerConnectionオブジェクトを作成する他に、①で取得したMediaStreamオブジェクトからMediaStream.getTracks()メソッドでMediaStreamTrackオブジェクトを取得し、RTCPeerConnection.addTrack()メソッドでこれから送信する音声・映像をセットしています。
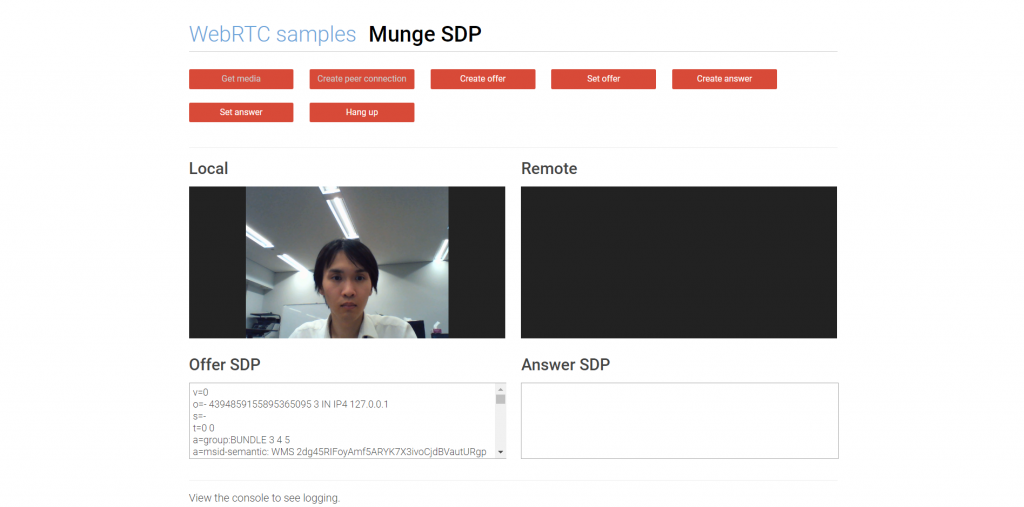
③[Create offer]ボタン
SDPと呼ばれる文書をoffer側(今回はローカル側)で作成します。SDPについての詳細な説明は今回省きますが、WebRTC接続にはお互いの内部情報をやりとりする必要があり、SDPはそれを表現するプロトコルです。
async function createOffer() {
try {
const offer = await localPeerConnection.createOffer(offerOptions);
gotDescription1(offer);
} catch (e) {
onCreateSessionDescriptionError(e);
}
}
function gotDescription1(description) {
offerSdpTextarea.disabled = false;
offerSdpTextarea.value = description.sdp;
}
SDP offerはRTCPeerConnection.createOffer()メソッドで作成します。
ここでは更に、作成したSDPをtextarea要素で表示しています。
④[Set offer]ボタン
作成したSDP offerをRTCPeerConnectionオブジェクトにセットします。
async function setOffer() {
let sdp = offerSdpTextarea.value;
const offer = {
type: 'offer',
sdp: sdp
};
console.log(`Modified Offer from localPeerConnection\n${sdp}`);
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars
const ignore = await localPeerConnection.setLocalDescription(offer);
onSetSessionDescriptionSuccess();
} catch (e) {
onSetSessionDescriptionError(e);
}
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars
const ignore = await remotePeerConnection.setRemoteDescription(offer);
onSetSessionDescriptionSuccess();
} catch (e) {
onSetSessionDescriptionError(e);
}
}
ローカル側はRTCPeerConnection.setLocalDescription()、リモート側はRTCPeerConnection.setRemoteDescription()でSDP offerをセットします。
今回は自分同士の接続なので気にしなくてよいのですが、本来リモートはSDP offerを知らないはずなので、SDPを伝達するためにシグナリングサーバーと呼ばれるものが必要になってきます。これについては次回以降で詳しく解説する、かも…?
また、SDP offerをセットした後、リモート側のonTrackイベントが発火します。イベント発火時の処理gotRemoteStream()は②でリモート側に設定しています。
function gotRemoteStream(e) {
if (remoteVideo.srcObject !== e.streams[0]) {
remoteVideo.srcObject = e.streams[0];
console.log('Received remote stream');
}
}
onTrackイベントが発火すると、通信相手が送信するMediaStreamオブジェクトの配列を受け取れるので、それをリモート側のvideo要素にセットしています。
ただし、この時点ではWebRTC接続が確立されていないので、セットした音声・映像が再生されることはありません。
⑤[Create answer]ボタン
SDPをanswer側(今回はリモート側)で作成します。
offerとanswerについての説明も次回以降をお楽しみに…!!
async function createAnswer () {
(中略)
try {
const answer = await remotePeerConnection.createAnswer();
gotDescription2(answer);
} catch (e) {
onCreateSessionDescriptionError(e);
}
}
function gotDescription2(description) {
answerSdpTextarea.disabled = false;
answerSdpTextarea.value = description.sdp;
}
SDP answerはRTCPeerConnection.createAnswer()メソッドで作成します。
③同様、作成したSDPをtextarea要素で表示しています。
⑥[Set answer]ボタン
作成したSDP answerをRTCPeerConnectionオブジェクトにセットします。
async function setAnswer() {
let sdp = answerSdpTextarea.value;
const answer = {
type: 'answer',
sdp: sdp
};
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars
const ignore = await remotePeerConnection.setLocalDescription(answer);
onSetSessionDescriptionSuccess();
} catch (e) {
onSetSessionDescriptionError(e);
}
console.log(`Modified Answer from remotePeerConnection\n${sdp}`);
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars
const ignore = await localPeerConnection.setRemoteDescription(answer);
onSetSessionDescriptionSuccess();
} catch (e) {
onSetSessionDescriptionError(e);
}
}
ローカル側はRTCPeerConnection.setRemoteDescription()、リモート側はRTCPeerConnection.setLocalDescription()でSDP answerをセットします。
ここまで完了すると後はWebRTCが勝手に接続試行を行ってくれ、成功するとリモート側のvideo要素で音声・映像の再生が始まります。
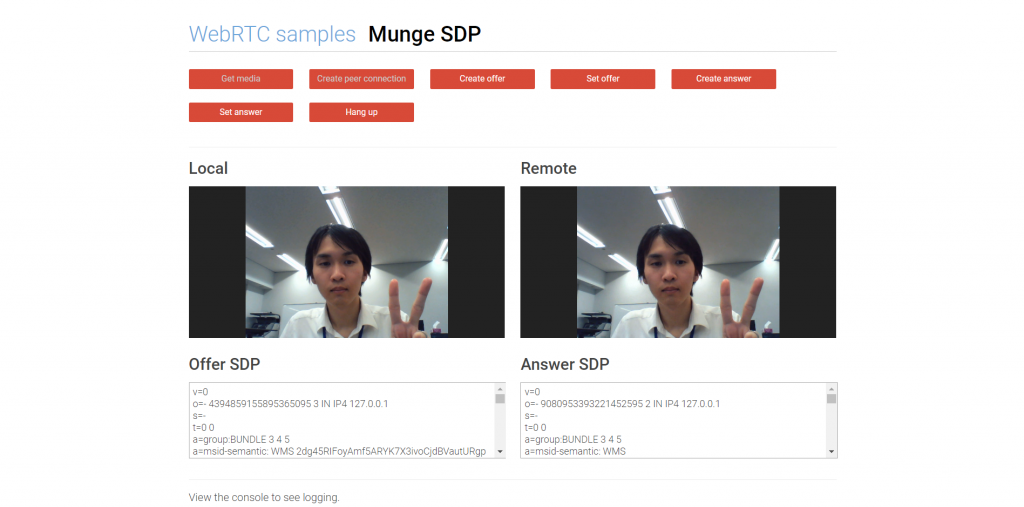
接続成功!
⑦[Hang up]ボタン
WebRTC接続を終了します。
function hangup() {
remoteVideo.srcObject = null;
console.log('Ending call');
localStream.getTracks().forEach(track => track.stop());
sendChannel.close();
if (receiveChannel) {
receiveChannel.close();
}
localPeerConnection.close();
remotePeerConnection.close();
(以下略)
ローカル・リモート共にRTCPeerConnection.close()メソッドでWebRTC接続を閉じます。
お疲れ様でした。
さて、いかがでしたでしょうか。
単純なP2Pであれば、WebRTCは誰でも簡単に利用することができる優れものです。
今後も『ReDois』やWebRTCについて継続的に発信していきます。
お楽しみに!

